What is a pediatric non-verbal disorder?
The signs and symptoms of pediatric minimally verbal autism do not match those of any well-described condition and currently there is no formally accepted diagnosis. Q BioMed has worked with 7 Autism Centers to establish a differential diagnosis that can be relied on for clinical trials, and we are grateful to the time and interest each center showed in wanting to help this underserved group of children.
Pediatric minimally verbal autism is accompanied with developmental delay, most notably where the toddlers never speak or will start speaking and then regress.
What causes non-verbal disorder?
Causes of pediatric minimally verbal autism have been linked to several complications that range from a specific mutated gene as with Fragile X Syndrome, Rett Syndrome, or SATB2 Syndrome; or it may arise from autoimmunity, where the body’s immune system is attacking parts of the brain. Trauma, microbial infections and environmental factors have also been linked to pediatric minimally verbal autism.
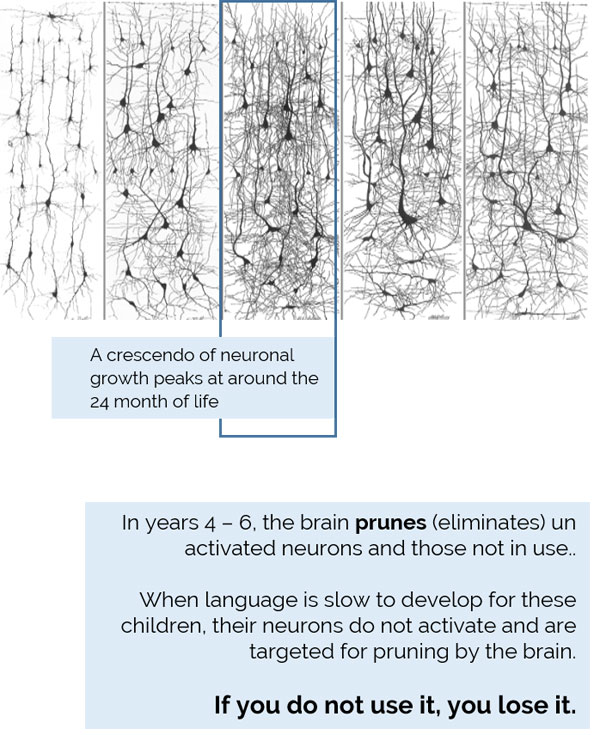
Studies from multiple researchers have confirmed that by the age of 7, children who have not developed language have significantly smaller cortex regions of the brain – the area responsible for language. And a general consensus is that if a child does not speak by the time they are 7, they will never develop spoken language. Ongoing research is helping to further explain the root cause of why children become non-verbal or minimally verbal for the rest of their lives.
Who is most likely to get non-verbal disorder?
Children born into families where there is a genetic history of autism or epileptic spectrum disorders or that have a sibling that has been diagnosed with an autistic or epileptic spectrum disorder have a much higher chance of becoming non-verbal.
Also, newborns identified with a mutated gene that leads to a known disease that affects language development are of course at high risk.
Prevalence
Among the >60,000 US children who develop Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) every year, about 20,000 become non-verbal.
Current standard of care
Of the estimated 20,000 who become non- or minimally verbal, they will often require assisted living for the rest of their life. The lifetime cost of that care is estimated at $5 million per person. Cognitive intervention is the only form for treatment that has shown to help improve speech capability and social interaction, however, it has not been able to alleviate the lifetime burden of $5 million per person for cost of care, and most children regress when intervention is stopped.
No therapies are currently available to treat this condition.

The hard facts and emotional truth
Currently, there are no drugs available to treat this condition. As a result, lifetime costs of assisted living and supplemental healthcare average $5 million per person. This is compounded by an additional $5 million during the lifespan of the person due to loss in productivity. These assessments of course cannot measure the severe emotional strain of never talking with your child.
Pediatric minimally verbal autism is rare and limited to approximately 20,000 children a year in the US and about the same in Europe.
Method of action
QBM-001 is designed to address multiple problems. One, it is designed to lower neurotoxins that build up in children with pediatric minimally verbal autism. Two, it may protect against signals that cause healthy neurons to die. And three, it may lower inflammation in the brain. Collectively, these effects are designed to alleviate the condition and allow toddlers to actively develop language and speech, and avoid life-long speech and intellectual disabilities caused from being non-verbal.


 .
.