What is liver cancer?
The liver is the football-sized organ in the upper right area of the belly. Symptoms are uncommon in the early stages of liver cancer. Later, symptoms may include weight loss, belly pain, vomiting, and yellowed skin. Treatments vary but may include removal of part of the liver, transplant, chemotherapy, and in some cases radiation.
What causes liver cancer?
Primary liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma) tends to occur in livers damaged by birth defects, alcohol abuse, or chronic infection with diseases such as hepatitis B and C, hemochromatosis (a hereditary disease associated with too much iron in the liver), and cirrhosis.
Who is most likely to get liver cancer?
In the United States, the average age at onset of liver cancer is 63 years. Men are more likely to develop liver cancer than women, by a ratio of 2 to 1. In the United States, liver cancer rates are highest in Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders. White Americans have the lowest risk for liver cancer. Chronic infection with Hepatitis B virus (HBV) or Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is the most common liver cancer risk factor. These infections lead to cirrhosis of the liver (see below).
What are the symptoms of liver cancer?
Symptoms are uncommon in the early stages of liver cancer. Later, symptoms may include weight loss, belly pain, vomiting, and yellowed skin.
RADIATION
High-energy x-rays or otherparticles destroy cancer cells
DRUG TREATMENT
Tryosine kinase inhibitor
antineoplastic agent, Nexavar™
SURGICAL
Hepatectomy or liver transplantation
CHEMOTHERAPY
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and
microwave therapy
THERMAL
Percutaneous ethanol injection
Uttroside-B chemotherapeutic
P Uttroside-B appears to affect phosphorylated JNK (pro survival signaling) and capcase activity (apoptosis inliver cancer)
- A natural compound
- Fractionated Saponin derived from S. nigrum
- Small molecule
- Steroid Glycosided
Uttroside-B increases the cytotoxicity of a variety of liver cancer cell types
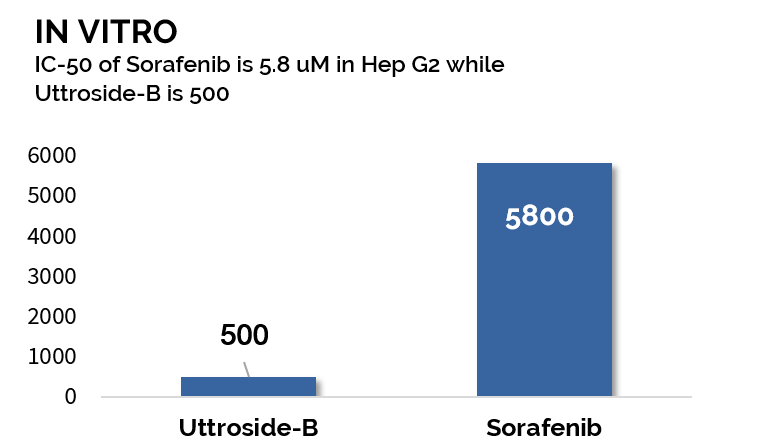
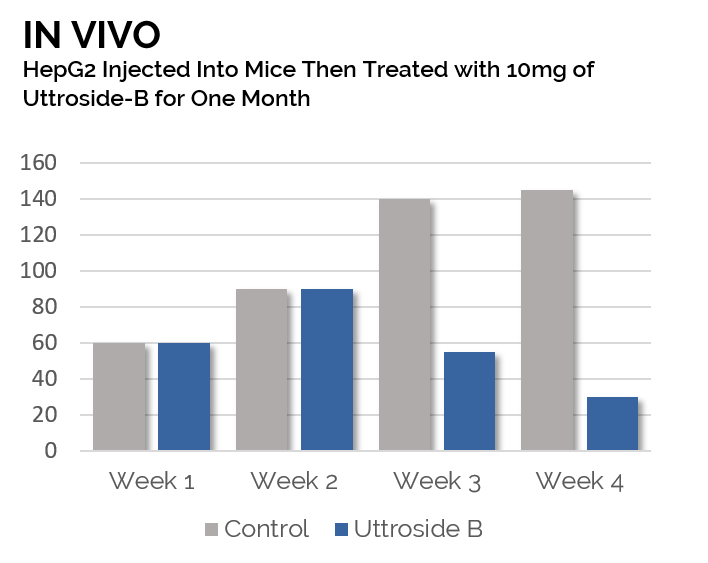
- Up to 10x more potent than Sorafenib in pre clinical studies
Cytotoxicity specific to cancerous liver cells
Provisional patent filed
IND Ready Q4 2020